What the VIX Measures (and Why It Moves)
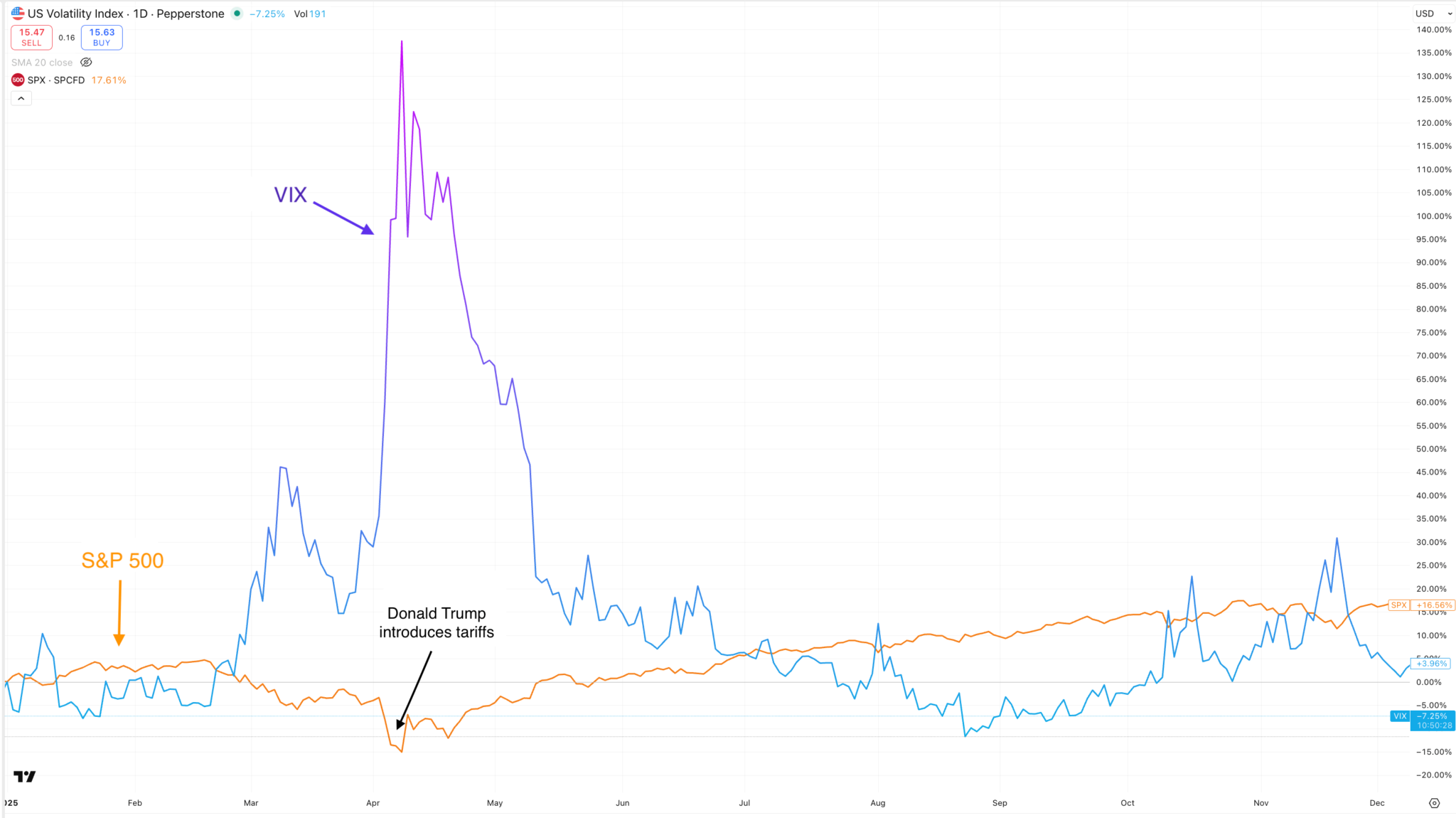
The VIX isn’t a “normal” index like the S&P 500 — it measures expected volatility, not price direction. When investors become nervous, demand for S&P 500 options rises, implied volatility increases, and the VIX typically climbs. When markets calm down, implied volatility falls and the VIX drops.
In practice, the VIX often rises during market sell-offs and major risk events — which is why it’s widely known as a fear gauge. Importantly, it’s forward-looking, reflecting what the options market expects over roughly the next month, not what volatility was in the past.
How You Can Trade the VIX
You can’t buy the VIX directly. Instead, traders gain exposure through derivative or packaged products, depending on the broker and region. The most common options include:
- VIX options – popular for hedging and event-driven trades
- VIX futures – direct exposure, but more complex and expiry-based
- VIX ETFs/ETNs – packaged products linked to VIX futures
- VIX CFDs – common outside the US; simpler access but often spread-based
- Synthetic volatility indices—broker-created products that simulate volatility (not tied to CBOE markets)
Why Traders Use the VIX
Most VIX traders fall into one of two groups:
Hedgers
When markets drop hard, volatility usually rises. That’s why many investors use VIX products to offset downside risk in equity-heavy portfolios. For example, if your portfolio is mostly US stocks and you expect turbulence, a VIX position may help reduce the impact of a drawdown.
Volatility Traders
Some traders don’t hedge — they trade volatility itself. VIX spikes can create short-term momentum opportunities, but they also come with sharper moves, wider spreads, and higher execution risk.
Advantages of Trading the VIX
Trading the VIX gives traders a direct way to position for changes in market fear, uncertainty, and volatility — often behaving very differently from traditional assets.
Key advantages include:
- Direct volatility exposure: The VIX reflects expected volatility in the S&P 500, making it one of the clearest sentiment tools available
- Strong hedging value: VIX products often rise during sharp sell-offs, which can offset losses in equity exposure
- More opportunity during stress: Volatility products often become more active during major events, creating tactical trading setups
- Multiple ways to trade: You can choose options, futures, ETFs/ETNs, CFDs, or synthetic volatility indices depending on your region and strategy.
Disadvantages of Trading the VIX
VIX trading can be effective — but it’s also one of the most misunderstood areas of retail trading, and it comes with unique risks.
Main downsides to understand:
- Complex pricing: The VIX is an index, but most products track futures-based pricing, which can behave differently from spot VIX
- Fast moves (high risk): VIX products can spike and reverse quickly — losses can escalate rapidly without strict risk controls
- Costs can be higher than expected: Volatility spreads and financing can widen significantly during stress — when you most want to trade
- Not all “VIX products” are equal: Some brokers offer synthetic “VIX” indices that don’t track the real VIX closely.
How to Reduce Risk Using VIX Options
VIX options are often used as defined-risk hedges, because option buyers can cap their maximum loss at the premium paid.
- If you expect volatility to rise (often during market declines), traders commonly use VIX call options to hedge downside exposure
- If you expect volatility to fall, traders may use VIX put options to hedge strategies that benefit from high volatility.
This is one reason VIX options remain popular: they offer a structured way to trade volatility with clearer risk limits than leveraged spot products.
What to Look For in a Broker for Trading the VIX (2026)
Not all brokers offer the same volatility products — and “VIX trading” can mean very different instruments. Some brokers focus on regulated markets like options and ETFs, while others offer CFDs or synthetic volatility indices.
When choosing a broker in 2026, prioritise the factors that directly affect cost, execution, and risk control:
Product type
Start with what you actually want to trade:
- VIX options or VIX ETFs/ETNs
- VIX CFDs (often outside the US)
- Real market products vs synthetic volatility indices
Fees
Volatility products can be fee-sensitive. Compare:
- spreads and commissions
- options contract pricing
- withdrawal and inactivity fees
Platform quality (especially for options)
A strong VIX broker should offer:
- clean option chains
- clear Greeks / implied volatility data
- stable performance during volatility spikes
Research and macro tools
VIX trading is tied to macro events and sentiment — good brokers should provide:
- volatility research
- market news + macro calendars
- volatility monitoring features
Risk controls
Volatility moves fast. Look for:
- stop-loss / take-profit support
- margin alerts and transparent leverage rules
- clear risk disclosures and position controls
Final Thoughts
Trading the VIX can be useful for both speculation and hedging, but volatility products behave differently from standard markets and carry higher risk — especially through options, futures, or leveraged CFDs. The key is choosing a broker that gives you the right VIX product access, transparent costs, stable execution, and strong risk controls. If you’re new to volatility trading, start small, use defined-risk tools, and treat the VIX as a strategic instrument — not a shortcut to fast profits.